FOURTH QUARTER OF 2021
I. GLOBAL SITUATION
During this fourth quarter of 2021, the global situation regarding the price of raw materials for the manufacture of feed has not improved. This means that farms use more affordable but poorer quality ingredients in their formulas, such as raw materials with high percentages of broken grain and dust.
This situation allows fungi and bacteria to grow more easily. In addition to reducing the nutritional value of the substrate, these microorganisms are the source of infections and produce toxins such as mycotoxins, which affect the health of animals. For this reason, there is a raising concern towards the control of microorganisms such as Salmonella in the feed, and high levels of aflatoxins, fumonisins and deoxynivalenol were detected in corn.
In the Northern hemisphere, humidity levels increased, and temperatures decreased. This has led to an augment of problems related to coccidia, necrotic enteritis, fungal contaminations, and mycotoxins. This increase in environmental humidity is more severe in farms where the ventilation is reduced to maintain a suitable temperature for the animals without investing more in heating. Poor ventilation also resulted in the accumulation of ammonia in the farms.
In the Southern hemisphere, an increase in infectious diseases has been observed, particularly of viral problems that are transmitted by migratory birds that travel from North to South in search of a better weather.
II. QUERIES BY SECTOR
II.1. Poultry farming
Viral diseases
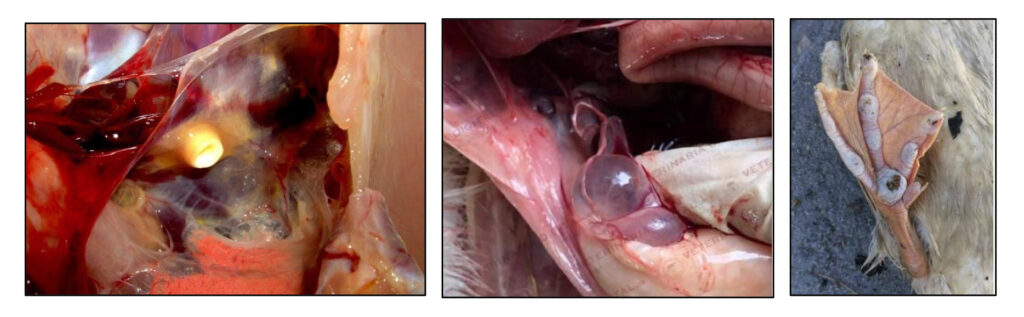
In the Southern hemisphere, poultry farms were affected by outbreaks of viral diseases transmitted by migratory birds, such as avian infectious bronchitis (IBV) and adenovirus. This has generated interest in finding natural ways to improve the effectiveness of vaccines. Another disease that has gained importance this quarter is avian flu in the Middle East, transmitted by migratory birds.
Bacterial diseases
Infectious toxic hepatoenteritis (HETI) has been reported all around the world. Concerns remain regarding the control of zoonosis-causing bacteria, such as Salmonella, E. coli, and Campylobacter. In addition to representing a danger to public health, these bacteria can have a negative impact on production performance. Salmonella causes birds to have biconcave nodules on the internal surfaces in birds, while E. coli has been associated with several cases of pericarditis.
There is interest in maintaining the balance of the intestinal flora to improve digestive health. This is because rapid transit and dirty egg problems have been observed in poultry farms.
Parasitoses
In the Northern hemisphere, outbreaks of coccidiosis and necrotic enteritis were diagnosed in broilers due to high humidity. Globally, outbreaks of blackhead disease (histomoniasis) were observed in turkeys.
Others
II.2. Pig farming
Actinobacillus suis is still present in pig farms around the world, causing immunodeficiency in affected pigs. This condition produces an increase in secondary problems such as pneumonia or Streptococcus infections, which take advantage of the animal’s weakness to cause diseases.
Other conditions observed in pigs were metritis-mastitis-agalactia (MMA) syndrome, related to the production of toxins at the digestive level, post-weaning diarrhea and other enteric problems that usually affect pigs in more advanced stages, such as porcine ileitis and dysentery, and the intestinal hemorrhagic syndrome.
II.3. Aquaculture
Tilapia production systems were affected by Streptococcus outbreaks. This bacterium usually affects the most advanced development stages, which is why it has a great economic impact. Temperature changes, high densities, inappropriate handling practices or any other factor that causes stress to animals can be the origin of one of these outbreaks.
On the other hand, there is a growing interest in the use of enzymes in aquaculture diets, additives that should be selected based on the diet and the particularities of the digestive system of the target species.
II.4. Ruminants
In ruminants, mastitis and problems caused by Actinobacillus lignieresii were reported.